Touch-typing, or keyboarding, isn’t perhaps, the most fun skill to learn, but it’s one of the most important. At the start of Media class, Gr. 3 students have been choosing between two, free, online programs, Dance Mat Typing or Big Brown Bear.
The focus of each 10 minute practice session is for students to use the correct fingers on the keys while improving their confidence and accuracy.
As an extension to Google for Education tools, students were asked to complete a survey that was created using Google Forms. Which of the two programs did students’ like better? Or did they like them both equally?
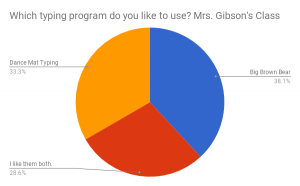
Google Forms turns the students’ responses into a spreadsheet that includes a pie chart. The pie chart above shows Mrs. Gibson’s class responses. Dance Mat Typing was the overall favorite of Gr. 3 students .
Students then learned how to create their own Google Sheets. They used the same data, but represented it in bar graph format.

D. Hixon, Mrs. Holt’s class
Next month, students will have a third choice, Typing Club. All three of these programs are free and can be accessed both at school and at home.
ISTE Standard for Students: 1c. Students use technology to seek feedback that informs and improves their practice and to demonstrate their learning in a variety of ways.